Data Storage
Introduction
Efficient data storage management is crucial for ensuring seamless operations and optimal performance within vuSmartMaps. With a dedicated module for HyperScale Data Store, administrators gain comprehensive control over organizing and accessing data.
The HyperScale Data Store offers a tiered approach, dividing data into Hot, Warm, and Archived storage states, each serving distinct purposes in data management and access. From restoring archived data to archiving and retrieving data, vuSmartMaps empowers users with intuitive tools and functionalities for streamlined data management, facilitating enhanced decision-making and productivity.
In the HyperScale Data Store, data is organized into three distinct tiers: Hot, Warm, and Archived Data Storage.
- Hot Data Storage: This tier is dedicated to storing recently accessed and critical data, providing high-speed access for immediate retrieval. Data in this state is maintained as per policy defined in data retention settings.
- Warm Data Storage: Intermediate storage for data accessed less frequently but remains relevant. It offers moderate-speed access to accommodate less frequent yet still pertinent data.
- Archived Data Storage: Archived Data Storage provides a long-term archival and storage solution for historical or rarely accessed data. Data stored in the Archived state cannot be queried directly and must be restored before it can be accessed. However, the data can be restored if required through the Data Storage module, offering a comprehensive data management solution that ensures data availability when needed while optimizing storage costs.
Managing Data Storage
The Data Storage page can be accessed from the platform's left navigation menu by navigating to Data Management > Data Storage.
The landing page on clicking the Data Storage looks like the following:
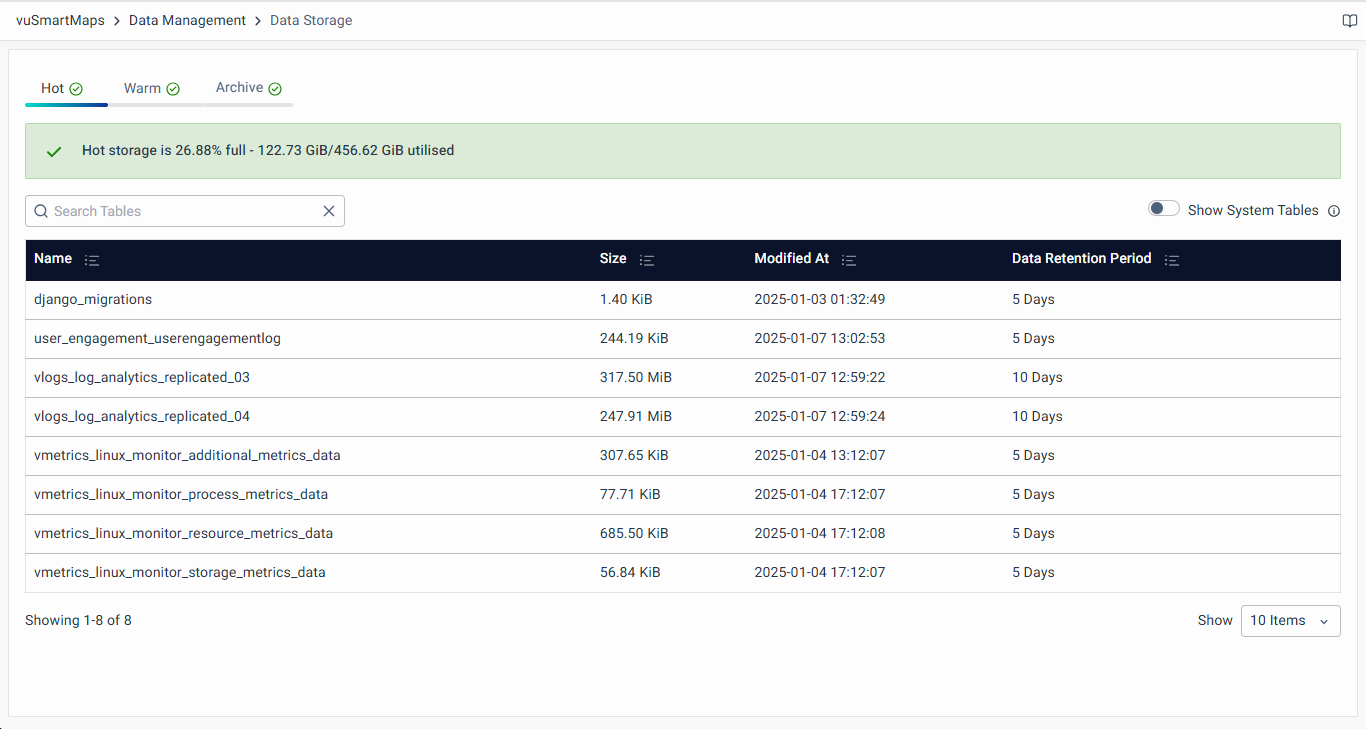
In the HyperScale Data Store, three dedicated tabs are available for Hot, Warm, and Archived Data Storage.
In the Hot, Warm, and Archived data storage tabs, you can find a list of available data tables in the Hot state, showing their name, size, last modified time, and data retention period. After the completion of this period, the data in the table will be removed/moved to other tiers, depending on the retention policy configured. Additionally, for each storage tab, memory utilization is displayed at the top, showing both the actual memory used and its percentage of the total available storage. This memory utilization is color-coded for clarity, with different thresholds for each storage state:
- Hot & Warm Storage:
- Warning Threshold: 50% of the total memory
- Critical Threshold: 80% of the total memory
- Archived Storage:
- Warning Threshold: 80% of the total memory
- Critical Threshold: 90% of the total memory These thresholds are visually represented with color coding to alert administrators of the current memory status in each storage state.
- Hot storage is mandatory and cannot be disabled.
- If the Warm or Archive storage is not enabled, a message stating, "Disk is disabled in this system" will be shown.
- If storage is enabled but data is inaccessible, the actual error message will be displayed, providing more detailed information.

Additionally, you can view System Tables by selecting the Show System Tables radio button. By default, system tables are hidden as they are used internally by the platform. Enabling this option will display system tables alongside regular data tables, providing a complete view of the data storage in use.
Restoring Archived Data
Archived Data can be restored to the main table, making the table queryable again.
On restoring data from Archival, the data will immediately be placed on the disk (Hot or Warm) from which it was originally archived. The restoration will move the data to the Main tables only, making it part of the original dataset.
It's important to note that the restored data will reside in the main table for the restore retention period (by default, 7 days, and configurable in the data retention module), after which it will be permanently deleted.
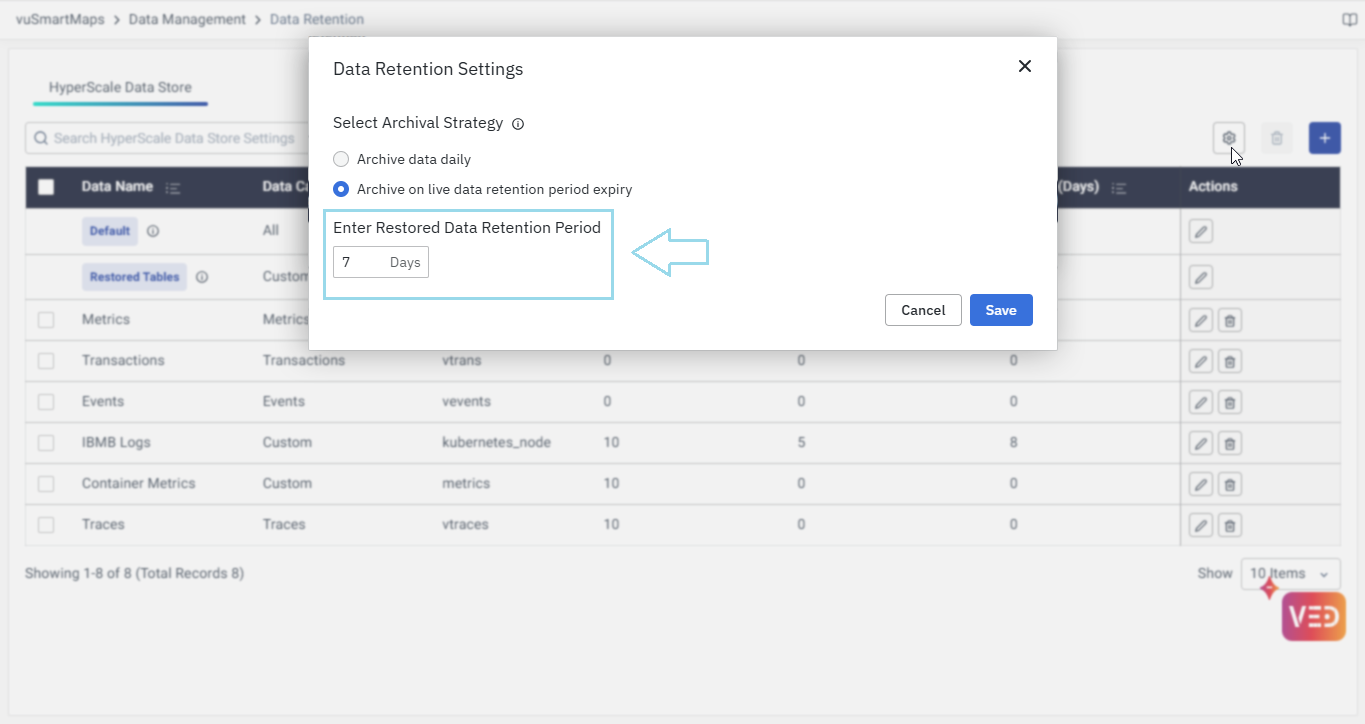
These values can be modified if necessary in the Data Retention Module to fit specific requirements.
As part of the schedule, the retention settings of the corresponding table are updated. This update ensures that data is retained for the defined retention period from the point of restoration, providing sufficient time for archival continuity and retention adherence. The default retention period is set to 7 days, but it is configurable in the data retention module.
A default data retention policy for restored data is available, which users can update according to their needs.
To restore archived data, follow these steps:
- Use the Restore button under the Actions column of the respective row in the Archive tab.
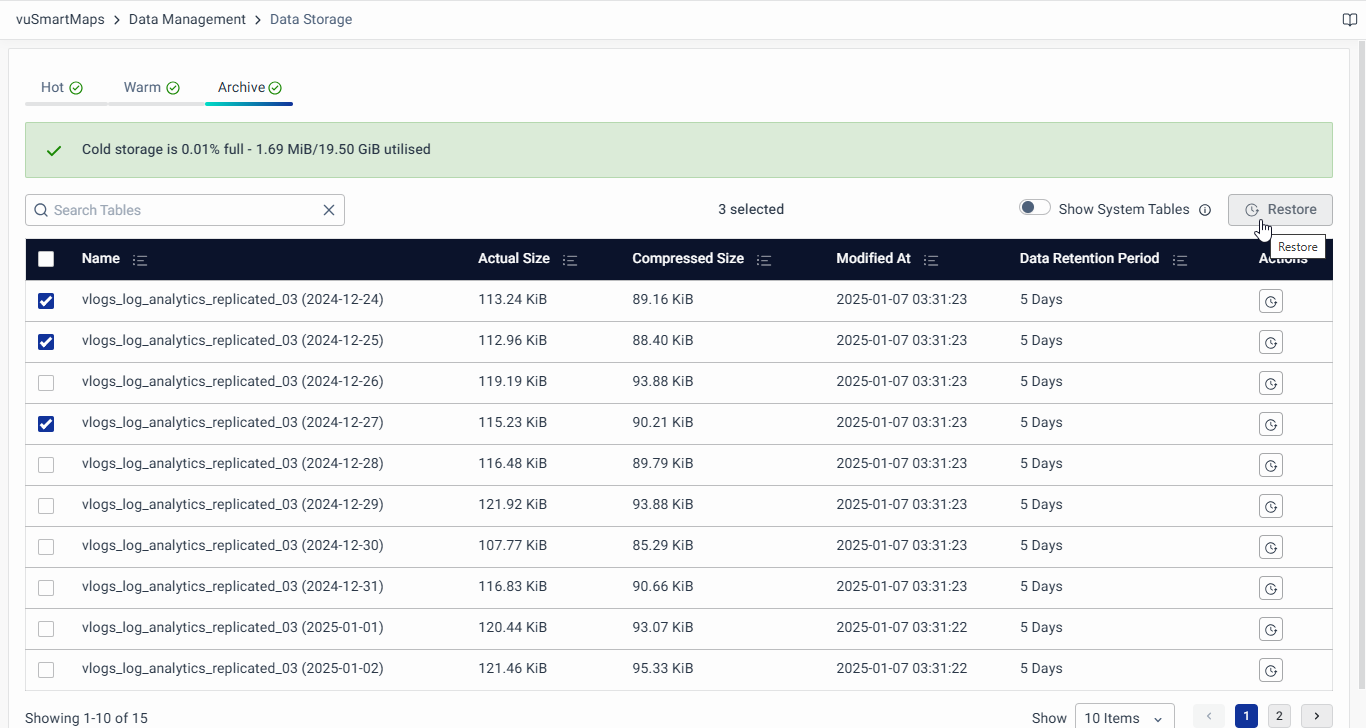
- Clicking on the Restore button will open a pop-up window. Click on Initiate Restore in the pop-up to restore the data from the archival store to the hot/warm disk.
- Similarly, for bulk restoration of data tables, select the respective rows, and use the Restore button located at the top of the table.
Restrictions on Initiating Restore: Users will be unable to initiate a restore operation for a file or set of files under the following conditions:
- Restore Already in Progress: If a restore operation is currently in progress according to system information.
- Data Already Present in Hot/Warm: If the data in the table is already present in Hot or Warm storage tiers. This is determined by checking for the presence of a table with the same name in Hot or Warm storage. Additionally, if the data is within the retention period specified in the data retention settings and is already stored in Hot or Warm storage.
- Insufficient Hot/Warm Storage Space: The restore operation will not proceed if it would leave less than 5% of Hot/Warm storage space free after restoration.
FAQs
As a data administrator, how can I ensure that critical data is always quickly accessible?
Critical and recently accessed data should be stored in the Hot Data Storage tier, which offers high-speed access for immediate retrieval. Ensure your data retention policies are configured to keep essential data in the Hot tier.
What should I do if I need to access data that has been moved to Archived Storage?
Use the Restore button in the Archived tab of the Data Storage module to move the data from Archived Storage to Warm Storage. Restored data will appear as restored-<table-name> in the Warm tab and will be retained for 7 days by default before permanent deletion.
How can I avoid running out of Warm Storage space when restoring archived data?
Before initiating a restore, check the memory utilization displayed at the top of the Warm Storage tab. A restore will be blocked if it reduces available Warm Storage space to below 5%.
As an IT operations manager, how can I automate the process of data archiving and retention?
Configure data retention policies to automate the transition of data between Hot, Warm, and Archived Storage, i.e., Data Archival. With this approach, less frequently accessed data is archived, ensuring data is managed according to the organization's requirements without manual intervention.
What can I do if I notice that data restoration operations are frequently failing?
Verify that there is sufficient space (at least 5%) in the Warm Storage tier before initiating restore operations. Check system logs for any errors related to data restoration and ensure that no other restore operations are currently in progress.
How can I quickly identify which data tables are due for archiving from Warm to Archived Storage?
In the Warm Storage tab of the Data Storage module, sort data tables by Last Modified Time or Size.
Identify tables that haven’t been accessed recently and manually move them to Archived Storage if needed.
How can I optimize data storage to efficiently manage high volumes of financial transaction data?
If you are dealing with high volumes of financial transaction data and need to optimize storage to ensure efficient data management and retrieval. Implement data archiving and compression strategies. Archive older transaction data to reduce storage costs and use compression techniques to optimize storage space.
What is the default retention policy for restored data?
By default, restored tables are retained in Warm Storage for 7 days, after which they are permanently deleted. You can modify this behavior using the Data Retention module.
Can I restore multiple archived data tables at once?
Yes, use the bulk restore option by selecting multiple rows in the Archived tab, and clicking Restore from the top menu. Each restored table will appear with the prefix restored- followed by the table name.
